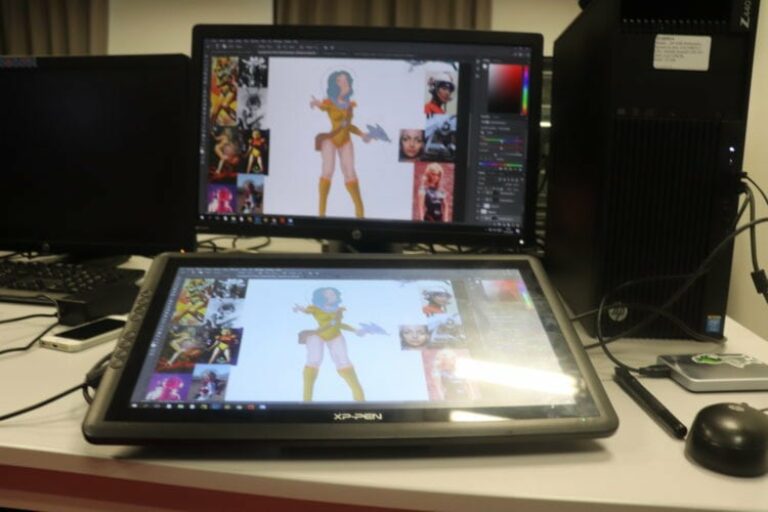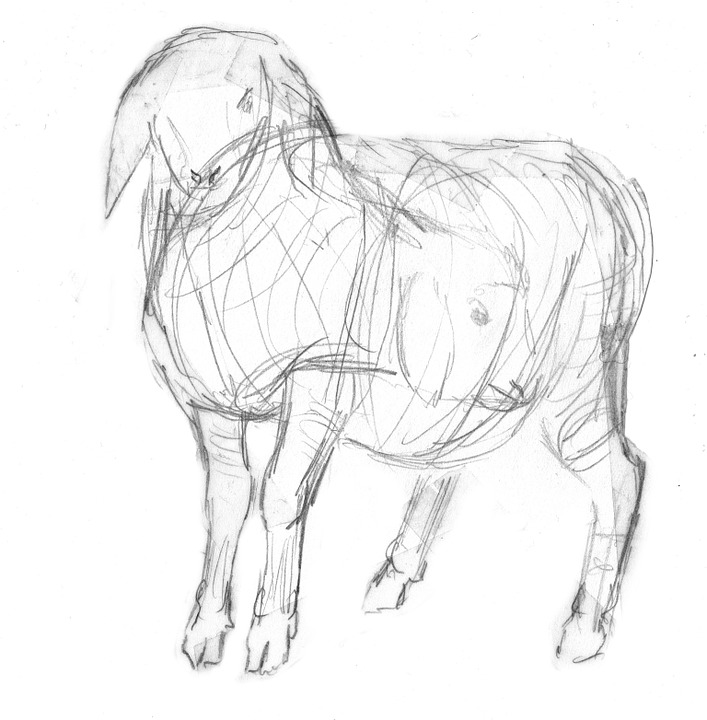
- Training 3D Animation & FX
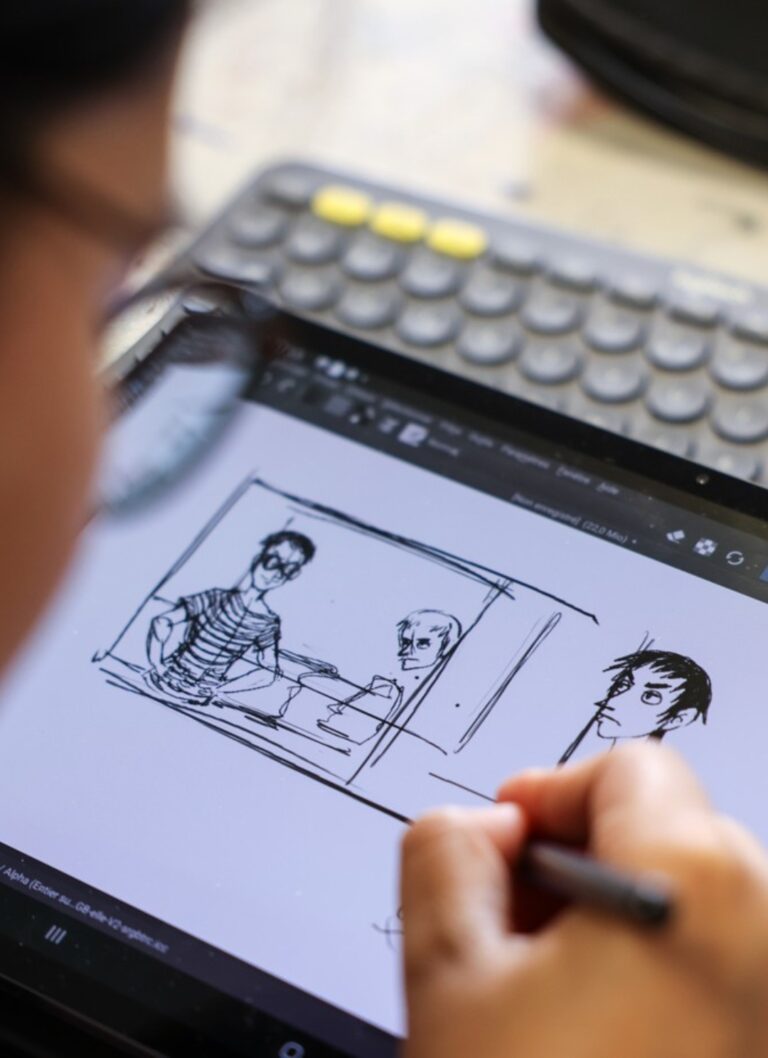
The roughman produces the first sketches of a project, which serve as a basis for the creative team
The role of the rough designer
As any golf fan will tell you, it’s best to keep the ball out of the rough (pronounced “reufs”), the part of the golf course that borders the course and is not mown as closely as the fairway and the edges of the greens. In the rough, the ball is difficult to play because it is generally embedded in the grass.
On the other hand, the roughman plays the role of scout and does not take the side paths by mistake. His rough sketches (drawings, illustrations, computer-generated images) for the production of an advertising campaign, or a film, allow the project to be visualised without already being locked into a definitive outline.
Clearly, the designer’s job is to visually represent a concept based on the broad outlines provided by the project’s decision-makers.
Skills and qualities
Rough artists must, of course, have a good pencil stroke, but they must also master the various drawing techniques, colour matching, DTP and computer graphics software, multimedia editing and be familiar with a wide range of visual codes.
A virtuoso draughtsman and creative artist, he or she must be able to change style depending on the product and the requirements of the creative team. Since their role is to convey the ideas of the designers as effectively as possible, their productions must be as close as possible to the concept imagined at the outset. Isn’t it said that a drawing is often more explicit than a long speech?
The rough artist works hand in hand with the art director. They have to be attentive to instructions and must be able to react quickly to deal with urgent situations, and to do this they need to be good listeners.
It’s not unusual for them to work on a wide variety of projects, including advertising campaigns, films, animated clips, video games, stands, shop windows and press illustrations.
Rough artists manage stress, work fast, are curious, analyse and design reactively. They need to know how to communicate and be convincing, while not becoming too formal when changes need to be made, as their creativity can be hampered if it conflicts with that of the decision-makers.
Career and development opportunities
Beaux-Arts, higher art diplomas or a BTS in visual communications are all possible routes to becoming a true professional.
The 3-year course of study after the baccalauréat (admission by application and interview) allows each student to make the most of their potential.
Rough designers work either as salaried employees in an agency or design studio, or more often as freelancers. In the latter case, they have to build up their own clientele among agencies and art directors, and receive highly variable remuneration. Rough artists are paid on an order-by-order basis, so it’s up to them to negotiate their rates with their clients on the basis of a number of factors (volume of plates to be produced, complexity of the job, etc.).
Rough artists may move on to become art directors or take up various positions in the graphic design and illustration industry.
Salary and career opportunities
On average, an experienced rough designer earns €2,700 gross per month (€1,500 to €2,000 gross for a beginner).
There are a wide range of career opportunities (packaging, advertising, video games, music videos, film, etc.), but places are fairly scarce and many roughmen wear several hats (illustrator or draughtsman).
Eventually, roughmen may move on to become Art Directors or apply for jobs in graphic design or illustration.